Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakamura, Toshihiro*; Adachi, Sadao*; Fujii, Minoru*; Sugimoto, Hiroshi*; Miura, Kenta*; Yamamoto, Shunya
Physical Review B, 91(16), p.165424_1 - 165424_8, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:56.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Semiconductor nanocrystals have unique electrical and optical properties, because of the quantum confinement effect, and the doping of impurities into nanocrystals. In this study, we investigated the photoluminescence (PL) properties of phosphorus- (P) and boron- (B) co-doped Si nanocrystals (Si NCs), which was synthesized using an ion implantation technique. The Si-NC size (average diameter: 3.5, 4.4, 5.2 nm) and the P and B ion doses (0.1-4.5 10
10 cm
cm )values were systematically varied. We find that the PL peak energy shifts to lower values with increasing the average diameters of Si NCs and PB ion dose. The results of PL measurements indicate that the PL spectra are due to the band-to-band transition at the reduced Si-NC band gap caused by the formation of impurity and the radiative transitions between defect- and/or impurity-related localized states. It was found that the PL properties can be controlled by varying the Si-NC size as well as the dopant concentration.
)values were systematically varied. We find that the PL peak energy shifts to lower values with increasing the average diameters of Si NCs and PB ion dose. The results of PL measurements indicate that the PL spectra are due to the band-to-band transition at the reduced Si-NC band gap caused by the formation of impurity and the radiative transitions between defect- and/or impurity-related localized states. It was found that the PL properties can be controlled by varying the Si-NC size as well as the dopant concentration.
Usui, Aya; Uno, Sadanori; Chiba, Atsuya; Yamada, Keisuke; Yokoyama, Akihito; Kitano, Toshihiko*; Takayama, Terumitsu*; Orimo, Takao*; Kanai, Shinji*; Aoki, Yuki*; et al.
Dai-27-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.118 - 121, 2015/03
no abstracts in English
 -implanted GaN film studied by a monoenergetic positron beam
-implanted GaN film studied by a monoenergetic positron beamLi, X. F.*; Chen, Z. Q.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, H.; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Applied Physics, 117(8), p.085706_1 - 085706_6, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.13(Physics, Applied)Vacancy-type defects in C -implanted GaN were probed using a slow positron beam. The increase of Doppler broadening S parameter indicates introduction of arge vacancy clusters. Post-implantation annealing at temperatures up to 800
-implanted GaN were probed using a slow positron beam. The increase of Doppler broadening S parameter indicates introduction of arge vacancy clusters. Post-implantation annealing at temperatures up to 800 C makes these vacancy clusters to agglomerate into microvoids. The vacancy clusters or microvoids show high thermal stability, and they are only partially removed after annealing up to 1000
C makes these vacancy clusters to agglomerate into microvoids. The vacancy clusters or microvoids show high thermal stability, and they are only partially removed after annealing up to 1000 C. Amorphous regions are observed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy measurement, which directly confirms that amorphization is induced by C
C. Amorphous regions are observed by high resolution transmission electron microscopy measurement, which directly confirms that amorphization is induced by C -implantation. The disordered GaN lattice is possibly due to special feature of carbon impurities, which enhance the damage buildup during implantation.
-implantation. The disordered GaN lattice is possibly due to special feature of carbon impurities, which enhance the damage buildup during implantation.
 Xe-higher fullerenes by ion implantation
Xe-higher fullerenes by ion implantationWatanabe, Satoshi; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Ishioka, Noriko; Matsuhashi, Shimpei; Muramatsu, Hisakazu*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 272(3), p.467 - 469, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.32(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Chen, Z. Q.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Sakai, Seiji; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Review 2005-001, TIARA Annual Report 2004, p.232 - 234, 2006/01
no abstracts in English
Pensl, G.*; Ciobanu, F.*; Frank, T.*; Kirmse, D.*; Krieger, M.*; Reshanov, S.*; Schmid, F.*; Weidner, M.*; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi; et al.
Microelectronic Engineering, 83(1), p.146 - 149, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:59.32(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)no abstracts in English
Nagata, Shinji*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Tokunaga, Kazutoshi*; Tsuchiya, Bun*; To, Kentaro*; Shikama, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 242(1-2), p.553 - 556, 2006/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.51(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 -implanted ZnO studied using a slow positron beam
-implanted ZnO studied using a slow positron beamChen, Z. Q.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 87(9), p.091910_1 - 091910_3, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:71.4(Physics, Applied)Zinc oxide crystals were implanted with N , O
, O , and co-implanted with O
, and co-implanted with O /N
/N ions. Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters upon implantation. In the N
ions. Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters upon implantation. In the N -implanted sample, these vacancy clusters are only partially annealed at 800
-implanted sample, these vacancy clusters are only partially annealed at 800 C as compared to their full recovery in the O
C as compared to their full recovery in the O -implanted sample, suggesting a strong interaction between nitrogen and vacancy clusters. At 1000-1100
-implanted sample, suggesting a strong interaction between nitrogen and vacancy clusters. At 1000-1100 C, nitrogen also forms stable complexes with thermally generated vacancies. To remove all the detectable vacancy defects, a high temperature annealing at 1250
C, nitrogen also forms stable complexes with thermally generated vacancies. To remove all the detectable vacancy defects, a high temperature annealing at 1250 C is needed. Furthermore, Hall measurements of this sample show n-type conductivity though nitrogen is expected as acceptors. On the contrary, in the O
C is needed. Furthermore, Hall measurements of this sample show n-type conductivity though nitrogen is expected as acceptors. On the contrary, in the O /N
/N co-implanted sample, most vacancy clusters disappear at 800
co-implanted sample, most vacancy clusters disappear at 800 C. Probably oxygen scavenges nitrogen to form N-O complexes and hence enhance the annealing of vacancy clusters. A highly compensated semi-insulating layer is formed in the co-implanted sample.
C. Probably oxygen scavenges nitrogen to form N-O complexes and hence enhance the annealing of vacancy clusters. A highly compensated semi-insulating layer is formed in the co-implanted sample.
Oshima, Takeshi
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (105), p.12 - 18, 2005/03
no abstracts in English
Chen, Z. Q.; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Xu, Y.; Naramoto, Hiroshi*; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Physical Review B, 71(11), p.115213_1 - 115213_8, 2005/03
Times Cited Count:106 Percentile:93.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ZnO crystals were implanted with 20-80 keV hydrogen ions up to a total dose of 4.4 10
10 cm
cm . Positron annihilation measurements show introduction of zinc vacancies, which are filled with hydrogen atoms. After isochronal annealing at 200-500
. Positron annihilation measurements show introduction of zinc vacancies, which are filled with hydrogen atoms. After isochronal annealing at 200-500  C, the vacancies agglomerate into hydrogen bubbles. Further annealing at 600-700
C, the vacancies agglomerate into hydrogen bubbles. Further annealing at 600-700  C causes release of hydrogen out of the bubbles, leaving large amount of microvoids. These microvoids are annealed out at high temperature of 1000
C causes release of hydrogen out of the bubbles, leaving large amount of microvoids. These microvoids are annealed out at high temperature of 1000  C. Cathodoluminescence measurements reveal that hydrogen ions also passivate deep level emission centers before their release from the sample, and lead to the improvement of the UV emission.
C. Cathodoluminescence measurements reveal that hydrogen ions also passivate deep level emission centers before their release from the sample, and lead to the improvement of the UV emission.
Uddin, M. N.; Shimoyama, Iwao; Baba, Yuji; Sekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Nath, K. G.; Nagano, Masamitsu*
Applied Surface Science, 241(1-2), p.246 - 249, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.11(Chemistry, Physical)Recently, much attention has been given on the synthesis and characterization of graphite-like B-C-N hybrid. Since graphite-like B-C-N hybrid may have semiconducting property, this material is interesting for applications to electronic and luminescent devices. In order to synthesize this material, borazine ion plasma was implanted in graphite at room temperature (RT) and 600  C. An ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) chamber with base pressure
C. An ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) chamber with base pressure  10
10 Pa was used for the experiment. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study suggested that B atoms in the deposited films are in a wide variety of atomic environment such as BC3, BN3 and B-C-N hybrid. The ratios of these coordinations strongly depend on the temperature during the ion implantation. It was found that the B-C-N hybrid is predominantly synthesized by the implantation at 600
Pa was used for the experiment. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) study suggested that B atoms in the deposited films are in a wide variety of atomic environment such as BC3, BN3 and B-C-N hybrid. The ratios of these coordinations strongly depend on the temperature during the ion implantation. It was found that the B-C-N hybrid is predominantly synthesized by the implantation at 600  C where the surface [B]/([B]+[C]+[N]) ratio ranges from 0.1 to 0.35. The results imply that it is possible to control the composition of B-C-N hybrid by changing the fluence of the ion plasma and the temperature of graphite during ion implantation.
C where the surface [B]/([B]+[C]+[N]) ratio ranges from 0.1 to 0.35. The results imply that it is possible to control the composition of B-C-N hybrid by changing the fluence of the ion plasma and the temperature of graphite during ion implantation.
Chen, Z. Q.; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Xu, Y.; Naramoto, Hiroshi; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 97(1), p.013528_1 - 013528_6, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:147 Percentile:96.39(Physics, Applied)Phosphorus ions were implanted into ZnO crystals with energies of 50-380 keV to a dose of 10 -10
-10 cm
cm . Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters after implantation. These vacancy clusters evolve to microvoids after annealing at a temperature of 600
. Positron annihilation measurements show the introduction of vacancy clusters after implantation. These vacancy clusters evolve to microvoids after annealing at a temperature of 600 C, and disappear gradually up to 1100
C, and disappear gradually up to 1100 C. Raman scattering measurements show the production of oxygen vacancies (V
C. Raman scattering measurements show the production of oxygen vacancies (V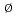 ). They are annealed up to 700
). They are annealed up to 700 C accompanying the agglomeration of vacancy clusters. The light emissions of ZnO are suppressed due to the competing nonradiative recombination centers introduced by implantation. Recovery of the light emission occurs above 600
C accompanying the agglomeration of vacancy clusters. The light emissions of ZnO are suppressed due to the competing nonradiative recombination centers introduced by implantation. Recovery of the light emission occurs above 600 C. The vacancy-type defects detected by positrons might be part of the nonradiative recombination centers. Hall measurement shows n-type conductivity for the P
C. The vacancy-type defects detected by positrons might be part of the nonradiative recombination centers. Hall measurement shows n-type conductivity for the P -implanted ZnO layer, which suggests that phosphorus is an amphoteric dopant.
-implanted ZnO layer, which suggests that phosphorus is an amphoteric dopant.
Chen, Z. Q.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yamamoto, Shunya; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.193 - 195, 2004/11
20-80 keV hydrogen ions were implanted into ZnO single crystals up to a total dose of 4.4 10
10 cm
cm . Positron annihilation measurements using a slow positron beam revealed introduction of vacancies after implantation, which are filled with hydrogen impurities. After annealing, these hydrogen filled vacancies grow into large hydrogen bubbles. At annealing temperature of 500-700
. Positron annihilation measurements using a slow positron beam revealed introduction of vacancies after implantation, which are filled with hydrogen impurities. After annealing, these hydrogen filled vacancies grow into large hydrogen bubbles. At annealing temperature of 500-700 C, these hydrogen impurities are released from the bubbles, and remain open microvoids. These microvoids are finally annealed out at about 1100
C, these hydrogen impurities are released from the bubbles, and remain open microvoids. These microvoids are finally annealed out at about 1100 C. The effects of hydrogen implantation on the light luminescence in ZnO will also be discussed.
C. The effects of hydrogen implantation on the light luminescence in ZnO will also be discussed.
Kasukabe, Yoshitaka*; Wang, J. J.*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Fujino, Yutaka*
Thin Solid Films, 464-465, p.180 - 184, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Wang, J. J.*; Kasukabe, Yoshitaka*; Yamamura, Tsutomu*; Yamamoto, Shunya; Fujino, Yutaka*
Thin Solid Films, 464-465, p.175 - 179, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.12(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yokota, Wataru
Kigyo Sapoto Gumma, P. 12, 2004/06
no abstracts in English
Okoshi, Kiyonori; Takada, Isao; Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Uno, Sadanori; Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Sakai, Takuro; Tajima, Satoshi
Dai-16-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.36 - 39, 2004/02
no abstracts in English
 ion-implantation-induced defects in ZnO studied with a slow positron beam
ion-implantation-induced defects in ZnO studied with a slow positron beamChen, Z. Q.; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Yuan, X. L.*; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 16(2), p.S293 - S299, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:71.56(Physics, Condensed Matter)Undoped ZnO single crystals were implanted with multiple energy N ions ranging from 50 to 380 keV with dose from 10
ions ranging from 50 to 380 keV with dose from 10 /cm
/cm to 10
to 10 /cm
/cm . Positron annihilation measurements show that vacancy defects are introduced in the implanted layers. The concentration of the vacancy defects increases with increasing ion dose. Annealing behavior of the defects can be divided into four stages, which correspond to the formation and recovery of large vacancy clusters, formation and disappearance of vacancy-impurity complexes, respectively. All the implantation induced defects are removed by annealing at 1200
. Positron annihilation measurements show that vacancy defects are introduced in the implanted layers. The concentration of the vacancy defects increases with increasing ion dose. Annealing behavior of the defects can be divided into four stages, which correspond to the formation and recovery of large vacancy clusters, formation and disappearance of vacancy-impurity complexes, respectively. All the implantation induced defects are removed by annealing at 1200 C. Cathodoluminescence measurements show that the ion implantation induced defects act as nonradiative recombination centers to suppress the ultraviolet emission. After annealing, these defects disappear gradually and the ultraviolet emission reappears, which coincides with positron annihilation measurement. The Hall measurements reveal that after N
C. Cathodoluminescence measurements show that the ion implantation induced defects act as nonradiative recombination centers to suppress the ultraviolet emission. After annealing, these defects disappear gradually and the ultraviolet emission reappears, which coincides with positron annihilation measurement. The Hall measurements reveal that after N -implantation, the ZnO layer still shows n-type conductivity.
-implantation, the ZnO layer still shows n-type conductivity.
 -implanted ZnO probed by a slow positron beam
-implanted ZnO probed by a slow positron beamChen, Z. Q.; Maekawa, Masaki; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yuan, X. L.*; Sekiguchi, Takashi*; Suzuki, Ryoichi*; Odaira, Toshiyuki*
Physical Review B, 69(3), p.035210_1 - 035210_10, 2004/01
Times Cited Count:91 Percentile:93.47(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Introduction and annealing behavior of defects in Al -implanted ZnO have been studied using energy variable slow positron beam. Vacancy clusters are produced after Al
-implanted ZnO have been studied using energy variable slow positron beam. Vacancy clusters are produced after Al -implantation. With increasing ion dose above 10
-implantation. With increasing ion dose above 10 Al
Al /cm
/cm the implanted layer is amorphized. Heat treatment up to 600
the implanted layer is amorphized. Heat treatment up to 600  C enhances the creation of large voids that allow the positronium formation. The large voids disappear accompanying the recrystallization process by the further heat treatment above 600
C enhances the creation of large voids that allow the positronium formation. The large voids disappear accompanying the recrystallization process by the further heat treatment above 600  C. Afterwards, implanted Al impurities are completely activated to contribute the n-type conduction. The ZnO crystal quality is also improved after recrystallization.
C. Afterwards, implanted Al impurities are completely activated to contribute the n-type conduction. The ZnO crystal quality is also improved after recrystallization.
Mizuhashi, Kiyoshi; Uno, Sadanori; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Chiba, Atsuya; Saito, Yuichi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Sakai, Takuro; Tajima, Satoshi
Dai-17-Kai Tandemu Kasokuki Oyobi Sono Shuhen Gijutsu No Kenkyukai Hokokushu, p.5 - 8, 2004/00
The three electrostatic accelerators were smoothly operated according to an allotted beam time. The total operation time for each accelerator in FY 2003 was 1,988 hours for the tandem accelerator, 2,286 hours for the single-ended accelerator and 1,773 hours for the 400kV ion implanter, respectively. The difference in the operating time between these accelerators dependent on the complexity of the ion source and the generating the quantities of ion species. And present state of 3MV tandem accelerator is reported.